Abstract
Detection of the JAK2 V617F somatic mutation has become standard care for diagnosing myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN), including polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET) and primary myelofibrosis (PMF). However, quantitation of V617F mutation allele burden (MAB) is not routinely evaluated, and the V617F MAB data are less frequently reported in the United States MPN population. We studied the correlation between V617F MAB and hematologic characteristics in our South Texas MPN patient population using a clinically validated allelic discrimination quantitative PCR (AD-qPCR) assay.
DNA was extracted from blood or bone marrow (BM) samples using the EZ1 DNA Blood Kit (Qiagen). AD-qPCR was performed on the ABI Prism 7900HT Sequence Detection System using TaqMan MGB probes (Applied Biosystems). The quantity of V617F MAB was determined by the comparative CT method (ΔΔCt method). The type of MPN, complete blood count (CBC) data, and clinical status were correlated with the V617F MAB. CBC data were collected on or near the date of JAK2 V617F MAB testing. Correlation and means comparison between V617F MAB and clinical data were analyzed by the Pearson correlation coefficient and t - Test, respectively.
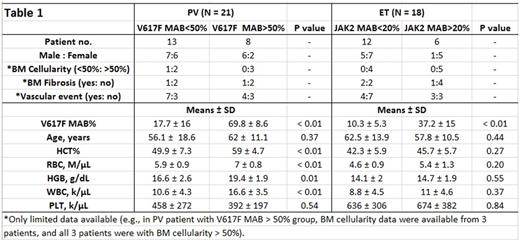
Of 638 blood and BM samples tested for V617F MAB due to clinical suspicion of MPN, 43 patients with detectable V617F allele and available hematologic data were included in this study. Fifteen of 43 patients had more than one specimen tested for the V617F MAB. For each of these 15 patients, only one representative V617F MAB result was included in this study. Among 43 MPN patients, 21 were diagnosed as PV, 18 ET, 4 myelofibrosis (3 PMF and 1 PV that progressed to fibrotic stage). Overall, the mean V617F MAB is higher in PV patients than ET patients (37.5% versus 19.2%). The mean V617F MAB of the 4 myelofibrosis patients is 55.2%. In PV patients, V617F MAB is positively correlated to hematocrit (HCT) level (R=0.72, P<0.01), RBC count (R=0.69, P<0.01), hemoglobin (HGB) level (R= 0.60, P<0.01), and white blood cell (WBC) count (R=0.76, P<0.01), but V617F MAB does not correlate to PV patient age or platelet (PLT) count. Based on the V617F MAB status, we divided PV patients into 2 groups: those with V617F MAB <50% versus those >50%. Compared to patients with lower V617F MAB (<50%), PV patients with higher V617F MAB (>50%) have significantly higher HCT, RBC, HGB, and WBC (Table 1) count. In ET patients, V617F MAB is positively correlated to RBC (R=0.61, P<0.01) but not to patient age, HCT, HGB, WBC, and PLT count. When ET patients were divided into groups with higher V617F MAB (> 20%) versus those with lower V617F MAB (< 20%), we did not find any significant differences between these 2 groups (Table 1). Interestingly, the single patient with PV that progressed to fibrotic stage showed extremely high V617F MAB (99%), which supports the literature findings of high V617F MAB being a risk factor for progression of PV to the fibrotic stage (Passamonti F et al. Leukemia 24:1574, 2010). For both PV and ET patients, the data of BM cellularity, BM fibrosis, and vascular event status were only available for a portion of patients, and their statistical power was limited. Thus, the information was displayed (Table 1) but not statistically analyzed. Similarly, due to the limited PMF case numbers in this study, statistical analysis was not performed on these patients.
Our study indicates that in PV patients, the V617F MAB was positively correlated with HCT, RBC, HGB as well as WBC, and a MAB greater than 50% reflected a more severe disease status. For ET and PMF, a larger scale study is needed to draw meaningful conclusions. Our data from a South Texas MPN population supports that JAK2 V617F MAB may provide meaningful insight into the clinical status of PV patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal